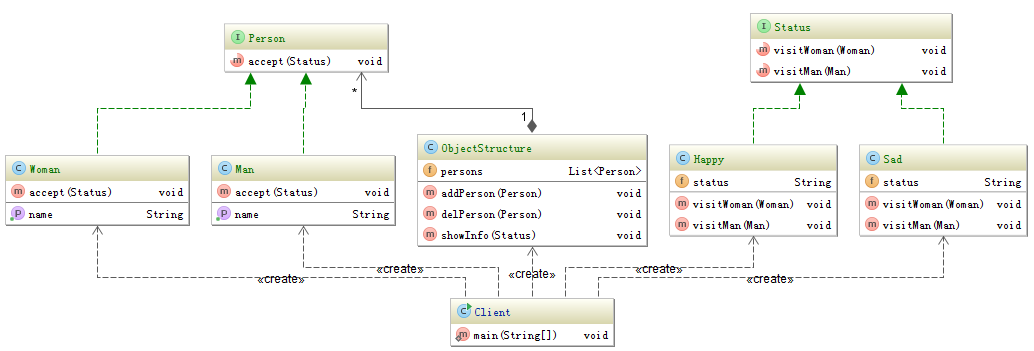
Java visitor pattern example 2017-02-23 08:03
The visitor is the most complex design pattern. This pattern shows us how to "visit" the elements of one structure without changing the code of element's. Add a new visitor when you want to add a new operation for these elements.
Person and the implements code.
public interface Person {
void accept(Status status);
}
public class Man implements Person {
private String name = "man";
@Override
public void accept(Status status) {
status.visitMan(this);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
public class Woman implements Person {
private String name = "woman";
@Override
public void accept(Status status) {
status.visitWoman(this);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
Status and implements code.
public interface Status {
void visitWoman(Woman woman);
void visitMan(Man man);
}
public class Happy implements Status {
private String status = "happy";
@Override
public void visitWoman(Woman woman) {
System.out.println("when " + woman.getName() + " " + status + " smile.");
}
@Override
public void visitMan(Man man) {
System.out.println("when " + man.getName() + " " + status + " laugh.");
}
}
public class Sad implements Status {
private String status = "sad";
@Override
public void visitWoman(Woman woman) {
System.out.println("when " + woman.getName() + " " + status + " cry.");
}
@Override
public void visitMan(Man man) {
System.out.println("when " + man.getName() + " " + status + " drink.");
}
}
Client and ObjectStructure code.
public class ObjectStructure {
private List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<>();
public void addPerson(Person person) {
persons.add(person);
}
public void delPerson(Person person) {
persons.remove(person);
}
public void showInfo(Status status) {
for (Person person : persons) {
person.accept(status);
}
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectStructure objectStructure = new ObjectStructure();
Person woman = new Woman();
Person man = new Man();
objectStructure.addPerson(woman);
objectStructure.addPerson(man);
Status happy = new Happy();
objectStructure.showInfo(happy);
Status sad = new Sad();
objectStructure.showInfo(sad);
}
}
The output is like following.
when woman happy smile.
when man happy laugh.
when woman sad cry.
when man sad drink.
Now you want add a new status (visitor). Add a new class HaveMoney like following.
public class HaveMoney implements Status {
private String status = "have money";
@Override
public void visitWoman(Woman woman) {
System.out.println("when " + woman.getName() + " " + status + " buy! buy! buy!");
}
@Override
public void visitMan(Man man) {
System.out.println("when " + man.getName() + " " + status + " invest.");
}
}
Change the code of Client.
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectStructure objectStructure = new ObjectStructure();
Person woman = new Woman();
Person man = new Man();
objectStructure.addPerson(woman);
objectStructure.addPerson(man);
Status happy = new Happy();
objectStructure.showInfo(happy);
Status sad = new Sad();
objectStructure.showInfo(sad);
// add new status
Status haveMoney = new HaveMoney();
objectStructure.showInfo(haveMoney);
}
}