Java abstract factory example 2016-12-15 02:57
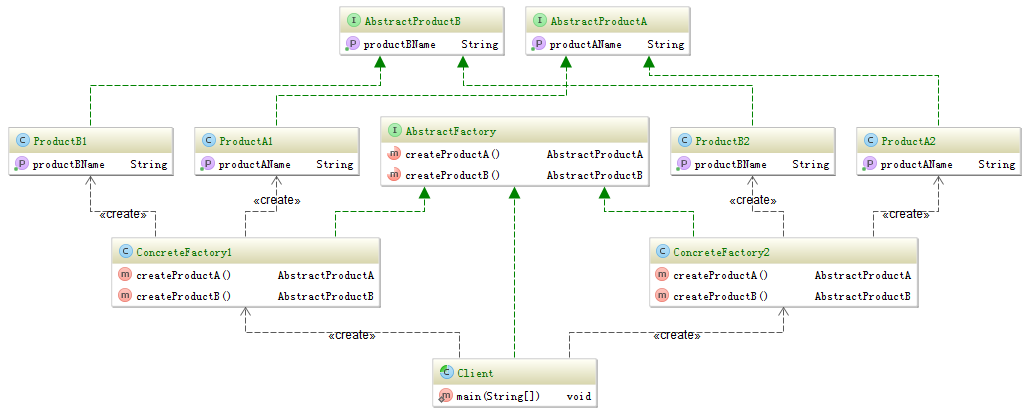
Abstract factory is one of the most popular design patterns. You can upgrade your program by adding concrete factory and without modifying the code. In this blog I will show you how it works. The diagram of it is like following.
1. Factory
public interface AbstractFactory {
AbstractProductA createProductA();
AbstractProductB createProductB();
}
public class ConcreteFactory1 implements AbstractFactory {
public AbstractProductA createProductA() {
return new ProductA1();
}
public AbstractProductB createProductB() {
return new ProductB1();
}
}
public class ConcreteFactory2 implements AbstractFactory {
public AbstractProductA createProductA() {
return new ProductA2();
}
public AbstractProductB createProductB() {
return new ProductB2();
}
}
2. Product
public interface AbstractProductA {
String getProductAName();
}
public interface AbstractProductB {
String getProductBName();
}
public class ProductA1 implements AbstractProductA {
@Override
public String getProductAName() {
return "This is ProductA1";
}
}
public class ProductA2 implements AbstractProductA {
@Override
public String getProductAName() {
return "This is productA2";
}
}
public class ProductB1 implements AbstractProductB {
@Override
public String getProductBName() {
return "This is productB1";
}
}
public class ProductB2 implements AbstractProductB {
@Override
public String getProductBName() {
return "This is productB2";
}
}
3. Client
public abstract class Client implements AbstractFactory {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String config = "1"; // you can get the value of config by reading config file
// String config = "2";
AbstractFactory factory;
switch (config) {
case "1":
factory = new ConcreteFactory1();
break;
case "2":
factory = new ConcreteFactory2();
break;
default:
throw new Exception("config error");
}
// start your business logic code
AbstractProductA productA = factory.createProductA();
AbstractProductB productB = factory.createProductB();
System.out.println("Product A : " + productA.getProductAName());
System.out.println("Product B : " + productB.getProductBName());
}
}
The aim of abstract factory is to create families of related products.. If you want create another families of product (Let's say ProductA3 and ProductB3). You just only need add ConcreteFactory3 and change the value of configuration. The most business logic code won't be changed.